 Home
Home
 Back
Back
| CHA2DS2-VASc Score | Number of Patients (n=7329) | Adjusted Annual Stroke Risk (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 422 | 1.3 |
| 2 | 1230 | 2.2 |
| 3 | 1730 | 3.2 |
| 4 | 1718 | 4.0 |
| 5 | 1159 | 6.7 |
| 6 | 679 | 9.8 |
| 7 | 294 | 9.6 |
| 8 | 82 | 6.7 |
| 9 | 14 | 15.2 |
This score is used for non-valvular atrial fibrillation and has certain guiding significance for anticoagulant therapy, as follows:
Score ≥2, high risk (annual stroke risk 2.2~15.2%), oral anticoagulant therapy is recommended;
Score = 1, moderate risk (annual stroke risk 1.3%), oral anticoagulant therapy or aspirin can be used;
Score = 0, low risk (annual stroke risk 0%), no antithrombotic therapy or aspirin is needed.
As shown in the figure below, choose an anticoagulant therapy strategy based on the CHADS2 score:
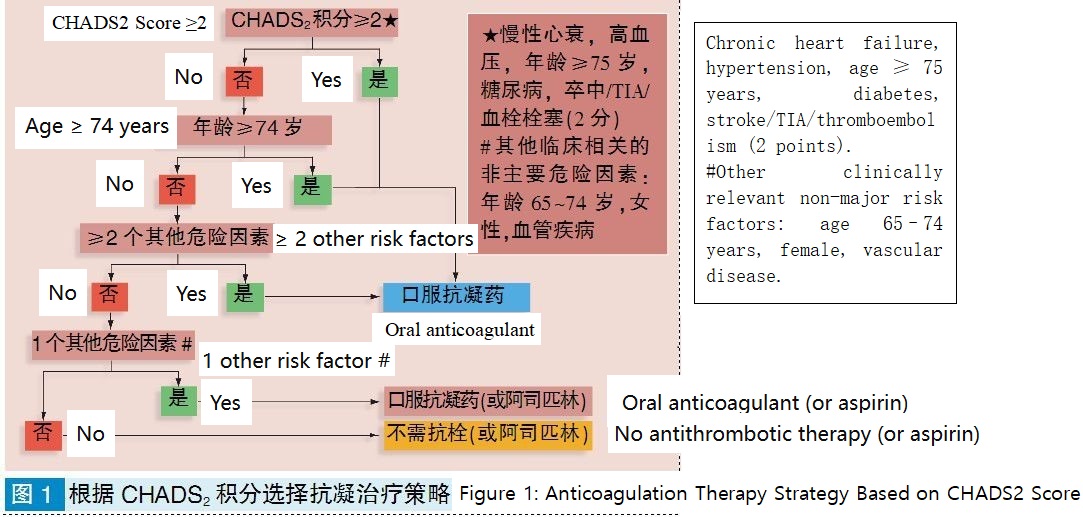
The CHA2DS2-VASc score modifies the CHADS2 score by changing the age ≥75 years from 1 point to 2 points, and adding three risk factors: vascular disease, age 65-74 years, and sex (female), thereby influencing the decision for anticoagulant therapy.