| Classification | Clinical Manifestations |
|---|---|
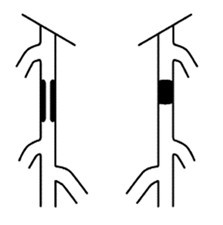
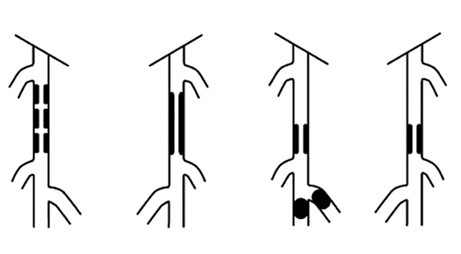
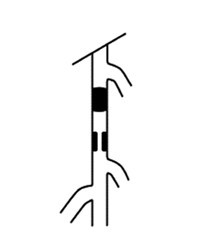
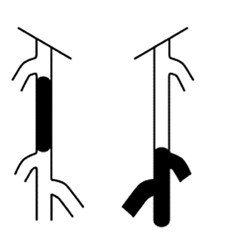
| Type A | 1. Single stenosis, length ≤ 10cm 2. Single occlusion, length ≤ 5cm
|
| Type B | 1. Multiple stenoses or occlusions, each ≤ 5cm 2. Single stenosis or occlusion (length ≤ 15cm), not involving the infrapopliteal artery 3. Single or multiple lesions, tibial artery not involved and can be used as a distal outflow tract for bypass surgery 4. Severely calcified occlusion (length ≤ 5cm) 5. Isolated popliteal artery stenosis
|
| Type C | 1. Multiple stenoses or occlusions, total length > 15cm, with or without severe calcification 2. Recurrent stenosis or occlusion requiring treatment after two endovascular interventions
|
| Type D | 1. Chronic total occlusion of the common femoral and superficial femoral arteries, > 20cm and involving the popliteal artery 2. Chronic total occlusion of the popliteal artery and the three below-knee branches
|
Explanation
"A" grade lesions are localized with good expected outcomes and should be treated with endovascular techniques;
"B" grade lesions are slightly extended, but considering the risks and expected patency of surgery versus endovascular treatment, endovascular treatment is still preferred;
"C" grade lesions have good outcomes with surgical reconstruction, but for patients with high-risk factors, minimally invasive endovascular techniques can be attempted;
"D" grade lesions should be treated surgically.
 Home
Home Back
Back